The European Credit Transfer System (ECTS)-more precisely known as the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System, is a points system that is used by universities across Europe to make education more compatible and comparable across borders. Seemingly complicated at first, the ECTS framework is quite easy to understand. This blog answers the most common questions on the European Credit Transfer System or ECTS.

IN THIS BLOG:
1. What is ECTS?
2. How do ECTS credits work?
3. Converting ECTS credits to study hours
4. Benefits of ECTS
5. Converting UK credits to ECTS credits
The ECTS framework assigns credit points to the workload that comes with study programs. Assigning credit points means that one module or course has the same value across different universities.
What is ECTS?
The European Credit Transfer System was established under the Bologna Process. The process was launched in 1998-99 to enhance the quality, compatibility and exchange conditions of European higher education systems within Europe and outside it. The Bologna Process has 48 European countries and several European organizations as its members.
Under the Bologna Process, a three-cycle degree structure (bachelors, masters, doctorate) and a shared credit system–the European Credit Transfer System were established. In 2010, when the European Higher Education Area (EHEA) was announced, the participating countries agreed to adopt the ECTS and the homogenous three-cycle degree structure.
How do ECTS credits work?
When a study program or module within the program is allotted ECTS credits or points, it indicates the workload that is required to complete the program or module. It is important to note that ECTS points only indicate the workload and not a grade.
60 ECTS points are usually worth a year of full-time study (or work, wherever applicable). Most of the time, this is divided into modules. If, for example, there are 4 modules in a year, each worth 15 ECTS points, the total credits add up to 60 ECTS points for that one complete year. The total workload of a study program in terms of ECTS points can be explained as–
- Bachelor’s degree – usually ranges from 180 ECTS (3 years full-time) to 240 ECTS (4 years full-time).
- Master’s degree – usually ranges from 60 ECTS (1 year full-time) to 120 ECTS (2 Years full-time).
- D. program – due to its flexible length and workload, it is difficult to assign an ECTS credit range to this program.
Have you taken the GMAT before?
Converting ECTS credits to study hours
60 ECTS credits or one year of full-time studies is usually defined between the range of 1,500-1,800 hours of study work implying that 1 ECTS credit point lies between 25 to 30 hours (except in the UK). The exact study hours vary depending on the country and can be categorized as follows-
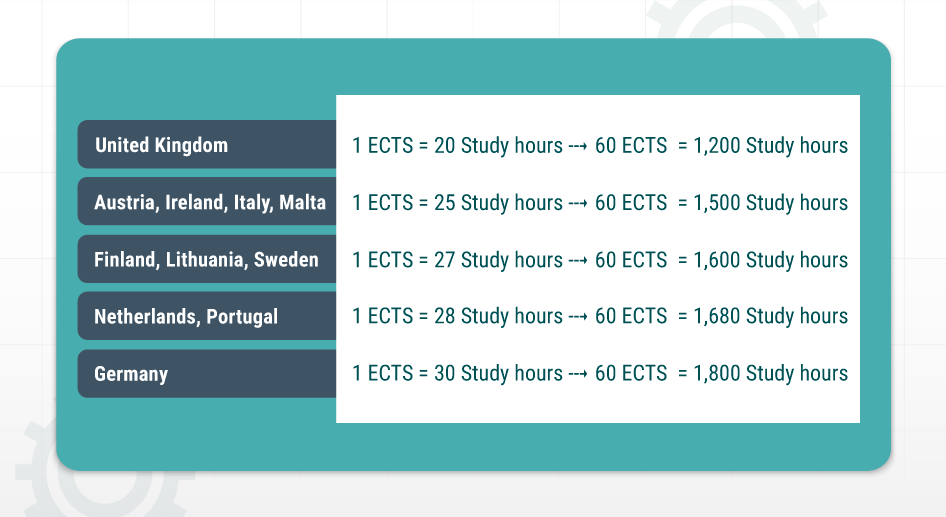
The aforementioned values are used just as a guide. Since they are inclusive of ‘contact hours’ (hours spent in classrooms), preparation and homework hours, etc., the individual study hours could be different. ECTS points are lower for part-time study programs, reflecting a lower workload.
Benefits of ECTS
ECTS credits serve to make higher education across Europe more compatible. Member countries of the European Higher Education Area (EHEA) use ECTS credits enabling students to work and study easily across Europe. ECTS credits are accepted by almost all European universities and many other institutions globally.
ECTS credit system enables students to-
- Transfer between universities without having to start over.
- Study abroad (as an exchange student)- for eg. 5 US college credits convert to 10 ECTS credits. This way, students in the US can attend a summer school or exchange semester at a European university and still use the credits at home.
- Applying for further education (eg. Master’s or Ph.D.)- in the same country or other countries.
- Find work across all EHEA countries.
The ECTS credit system is used by universities in all 48 member countries of the European Higher Education Area, or EHEA.
Have you taken the GMAT before?
Converting UK credits to ECTS credits
Although the UK is a part of the EHEA, credits are defined separately for the UK countries. For Scotland, the SCQF framework and for England, Northern Ireland and Wales, the CATS scheme is used for defining credits–though the underlying value is the same. The UK credit points and ECTS credit points have a simple conversion rate of 2 UK credits = 1 ECTS credit.
In recent years, European countries have seen an influx of international students owing to their world-class education and high standard of living. If you too are planning your higher education abroad, book a free fifteen-minute session with our counselor.









 BANGALORE
BANGALORE BHOPAL
BHOPAL CHENNAI
CHENNAI DELHI
DELHI FARIDABAD
FARIDABAD GURGAON
GURGAON GR. NOIDA
GR. NOIDA HYDERABAD
HYDERABAD INDORE
INDORE JAIPUR
JAIPUR KOLKATA
KOLKATA Kathmandu
Kathmandu LUCKNOW
LUCKNOW MUMBAI
MUMBAI NAVI MUMBAI
NAVI MUMBAI NOIDA
NOIDA PUNE
PUNE THANE
THANE Not in the list?
Not in the list?
Leave a Reply